Customer segment management: What you didn’t know your marketing analytics team was missing
Marketers are obsessed with measuring the results of their efforts, and rightly so. In all campaigns, there can be hefty amounts of time, energy, and money devoted to accurately capturing and reporting on an immense variety of marketing metrics — ROI, CTA, CTR, ROAS, CPA, SOV — the list is endless. However, many of these measures are largely tactical, with a focus on the performance of marketing campaigns and marketing channels.
But where is the customer in all these metrics? While many brands profess to be customer-centric, consider how they’re organized. Marketing departments have digital marketing teams, social media teams, advertising teams, product managers, and creative services teams, but few have what I would refer to as “customer teams”.
Measuring Value
In the first of a series of related articles, We’ll explore the concept of ‘customer segment management’ — an approach based on defining and measuring the aggregate value to the brand of specific and exclusive customer segments, as well as changes in customer behaviors and values over time. Customer segment management works best for brands with known customer data, where purchase activity can be tracked and analyzed at the customer record level.
The graphic below illustrates the ongoing process by which customer behaviors are analyzed, upside revenue potential is estimated, marketing program impacts and costs are forecasted, programs are executed, and results measured — at which point the process repeats itself.
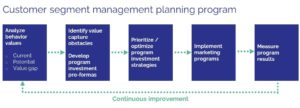
Let’s look at just one example of how to create customer segments and analyze behavior values.
Customer behavior
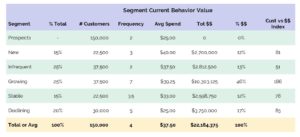
Because customer segment management is all about customer behaviors and their associated values, we first conduct a trend analysis. In this example, customers were scored on recency, frequency, and monetary value (RFM) in distinct twelve-month periods covering the last two years. For this example, we’ve put recency aside since it tends to be highly correlated with frequency. After several rounds of exploratory analysis, the following definitions were used to create the customer segments:

In the table below, segment behavior values for frequency and monetary value (in this case average transaction size) vary by segment. This insight alone is a key finding. Here, customers in the Growing customer segment are disproportionately contributing to revenue, an insight that would not have been uncovered without the customer segment management framework.
By leveraging this view of the segment’s current values and applying pro-forma adjustments to frequency and monetary values, we can arrive at reasonable forecast estimates for the potential value of each segment. In the next table, the cells highlighted in light blue represent the estimated change in behavior values. For instance, while the goal of a 40% increase in frequency from the Infrequent segment might seem aggressive, you can see from the table above that it equates to increasing frequency to 2.8 transactions/year from the current level of 2 transactions/year.
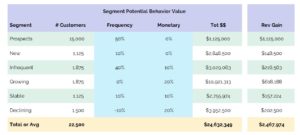
All told, these relatively modest behavior change goals would deliver an annual increase of ~$2.5MM, or an 11% year-over-year revenue growth rate.
The advantages of customer segment management are numerous:
- It is customer-centric, assigning customers to segments based on trends of their purchase behavior. Customer centricity forces organizations to consider their value propositions from the perspective of the customer, not the company
- It reflects the total impact of multiple marketing campaigns and tactics on customer behaviors and their values, adding a powerful new dimension of measurement
- It is particularly relevant in an omnichannel world since it captures all known customer purchase behavior regardless of channel
- It enables marketing resource allocation at the segment level, offering a very different view of the impact of different budgeting priorities
In the next installment of this series, we’ll continue to explore examples of how customer segment management could benefit your organization.
Read more articles about:
Location-based marketing contentSubscribe and get the latest updates
You may unsubscribe from our mailing list at any time. To understand how and why we process your data, please see our Privacy & Cookies Policy
Related resources
Location intelligence
Market Optimizer: Demo video
Market Optimizer allows users to strategically grow their network in existing markets while balancing revenue...
Fuel pricing
The Kalibrate news round-up: June 2025
In this monthly feature, we look across the industry and mainstream news to uncover stories of note that we think are...


